In the realm of nutrition, few beverages can rival the versatility and milk's nutritional value. Milk, often referred to as “nature’s perfect food,” has been a dietary staple for millennia, cherished not only for its creamy taste but also for its impressive nutritional profile. In this blog, we will uncover milk nutrition, the health benefits of milk, and inclusion in your daily diet.
So, if you’re ready to explore the versatile world of milk, keep scrolling.
Understanding Milk Nutrition
Milk is a nutrient-dense liquid that contains a wide array of essential nutrients necessary for the proper functioning of the human body. One cup of reduced-fat (2%) milk provides approximately 122 calories, 5 grams of fat, 12 grams of carbohydrates, and 8 grams of protein. It also offers a significant amount of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin A, vitamin D, riboflavin, vitamin B12, potassium, zinc, choline, magnesium, and selenium.
Components of Milk
Protein Power: Milk is your go-to source for some high-quality protein. Protein is a fundamental building block that plays a crucial role in the creation and repair of cells. It’s got all the essential amino acids, which is a fancy way of saying it’s super good for your muscles and all-around health. With 8 grams of protein per cup, milk is an ideal snack option, providing a well-balanced source of this vital nutrient. So, if you’re looking to beef up your muscles, milk’s got your back.
Carb Magic: Lactose, that’s the main carb in milk, is your speedy source of energy. That’s why it’s perfect for keeping up with those little kiddos who seem to have boundless energy.
Fats Galore: Now, the fat content in milk can change based on the type. Whole milk has more fat, while skim milk has, well, pretty much no fat. But, fats in milk help your body absorb those fat-soluble vitamins in milk like A, D, E, and K. So, it’s kind of like a vitamin booster.

The Alphabet of Vitamins in Milk
- Vitamin D: You might have heard of this one. Milk is often boosted with vitamin D. This little sunshine vitamin helps your bones stay strong and your immune system kickin'.
- Vitamin A: It's all about healthy skin and clear vision. Vitamin A is your skin's best friend and your eye's guardian angel.
- Vitamin B: You can find some B vitamins in milk like riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), and B12. They help you turn food into energy, keep your nerves in check, and even make those red blood cells.
Mighty Minerals
- Calcium: Milk is famous for this one. Calcium is what you need for strong bones and pearly whites. It’s like the building blocks for your skeleton.
- Phosphorus: It’s like calcium’s sidekick. Together, they make sure your bones are superhero-strong. Phosphorus also does other cool stuff like helping your body make DNA and RNA.
- Potassium: This mineral is the unsung hero. It’s all about heart health, blood pressure control, and making sure your muscles and nerves play nice.
Other important nutrients found in milk include zinc, choline, magnesium, and selenium.
Exploring the Health Benefits of Milk
Milk, we all know it’s that creamy goodness we pour over cereal or add to our morning coffee, but it’s way more than just a tasty beverage. It’s like nature's multivitamin! So, let’s break down why you should keep milk in your fridge for the yummy health benefits of milk.
Heart-Healthy Sip
Potassium in milk helps keep your blood pressure in check, lowering the risk of heart troubles. The unique combination of calcium, potassium, and magnesium found in milk is believed to reduce the risk of hypertension. Peptides derived from the digestion of casein, a milk protein, may also play a role in blood pressure regulation. Some studies even say milk might help keep heart diseases at bay.
Flex Those Muscles
Milk’s protein, especially the duo of casein and whey, is like a personal trainer for your muscles. It helps them grow and repairs them after a workout. Studies have shown that milk consumption after resistance exercise leads to increased muscle mass, strength gains, and fat loss. In older women, regular consumption of milk, and milk products has been associated with improved body composition and physical performance.

Milk Makes Your Bones a Solid
Calcium, the MVP of milk, keeps your bones strong and can prevent that dreaded osteoporosis. It’s like a shield for your skeleton. Furthermore, the high protein content contributes to bone growth and density, making it an excellent choice for maintaining bone health.
Keep the Pounds in Check
The combo of protein and fat in milk can help you feel full, so you're less tempted to munch on those not-so-healthy snacks. It's like your secret weapon in the battle of the bulge.
Get that Glowing Skin
Vitamin A in milk is your skin’s best friend. It keeps your skin cells in tip-top shape and fights off bad stuff that can lead to skin issues.
Say Cheese for Strong Teeth
Calcium in milk doesn’t just do wonders for your bones; it’s a tooth’s best buddy too. It helps keep those pearly whites strong and cavities at bay.
Milk: Your Post-Workout Buddy
After a sweaty workout, your body needs to recover. The mix of carbs, protein, and electrolytes in milk makes it a perfect post-workout drink. It helps your muscles heal and restock that energy reserve.
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that milk processing methods and types of milk can vary. Pasteurized milk undergoes a process that heats milk to destroy harmful bacteria, ensure safety, and extend shelf life. Homogenization, on the other hand, breaks down fat globules to create a consistent texture. These processing methods have no adverse effects on milk’s nutritional value.
Exploring Milk Varieties
There are various varieties of milk available, catering to different dietary preferences and nutritional needs. Whether you go for classic dairy or dive into the world of plant-based milk, there’s something to suit your needs. Here are the big players:
- Whole Milk: It’s like the full-fat party version of milk, rich and creamy, containing around 3.25% milk fat. It’s the most natural form of cow’s milk. Whole milk is a good source of essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D, but it’s also higher in calories and saturated fat compared to lower-fat options.
- Skim Milk (Fat-Free): It’s like the lean, mean version with all the goodness leaving it with less than 0.5% milkfat. This results in a significantly lower calorie and fat content while retaining most of the other essential nutrients found in milk, including protein, calcium, and vitamin D.
- 2% Milk (Reduced-Fat): Right in the middle - not too lean, not too creamy, contains about 2% milkfat. It strikes a balance between the richness of whole milk and the lower fat content of skim milk. It’s a popular choice for those looking to reduce their fat intake while still enjoying the taste of milk.
- 1% Milk (Low-Fat): 1% milk is a low-fat option, containing approximately 1% milk fat. It’s a lighter alternative to whole milk while maintaining essential nutrients. It’s a suitable choice for individuals looking to cut back on calories and saturated fat.
- Raw Milk: Raw milk is milk that is not pasteurized milk, a process of heating milk to kill harmful bacteria. Advocates of raw milk believe it retains more nutrients and enzymes, but it can also carry a higher risk of bacterial contamination. Many health authorities recommend against consuming raw milk due to safety concerns.
- Lactose-Free Milk: Lactose-free milk is regular cow’s milk that has been treated to break down lactose, making it suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance. It provides the same essential nutrients as regular milk but without the digestive discomfort that lactose intolerance can cause.
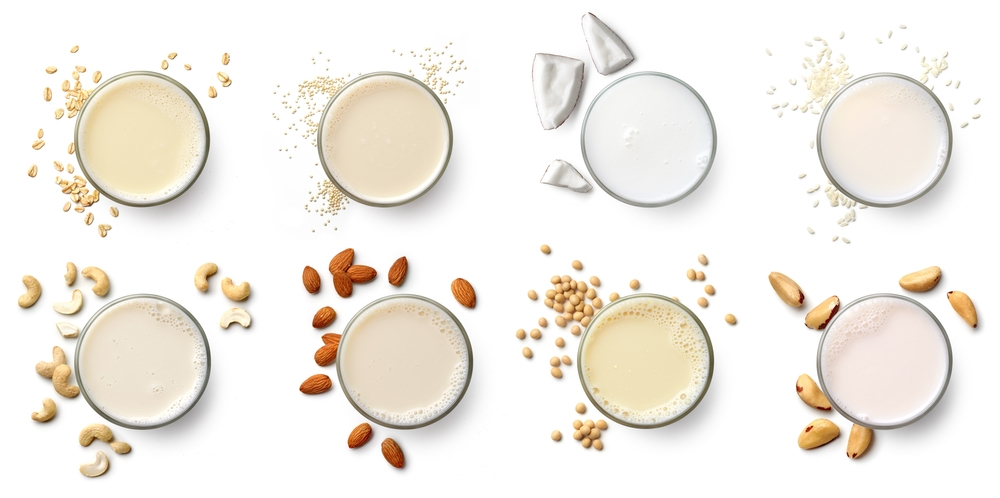

- Almond Milk: The non-dairy superstar that’s low in calories and perfect if you’re lactose intolerant or just nutty for nuts. Almond milk is a popular plant-based milk made from almonds. It’s typically lower in calories and saturated fat than cow’s milk but may be lower in protein unless fortified.
- Soy Milk: Another non-dairy option, soy milk is your plant protein buddy, made from whole soybeans. It’s a good source of protein, often fortified with vitamins and minerals to mimic the nutrient profile of cow’s milk.
- Oat Milk: Oat milk is made from whole oats and has gained popularity for its creamy texture and mild, slightly sweet taste. It’s often fortified with calcium and vitamins, making it a good option for those with dairy allergies or lactose intolerance.
- Coconut Milk: Coconut milk can refer to two different types. One is the thick, creamy liquid extracted from grated coconut flesh and used in cooking and baking. The other is the coconut milk beverage, which is a dairy alternative made from diluted coconut cream. The beverage form is often used in smoothies and coffee and is available in both sweetened and unsweetened varieties.
- Cashew Milk: Cashew milk is a creamy and mildly flavored dairy alternative made from blended cashews. It’s lower in calories and fat compared to whole milk and is often fortified with essential nutrients.
- Flax Milk: Flax milk is another plant-based milk made from flaxseeds. It’s a dairy-free and nut-free option that’s typically fortified with vitamins and minerals.
How To Add Milk To Your Diet?
Incorporating milk into your diet can be both delicious and nutritious. Here are several ways to include milk in your daily meals:
- Classic Glass of Milk: Enjoy a glass of milk on its own as a refreshing beverage. You can have it plain or with a touch of sweetness if you prefer, such as honey or a bit of chocolate or strawberry syrup.
- Cereal or Oatmeal: Pour milk over your morning cereal, granola, or oatmeal. It adds creaminess and complements the flavors of these breakfast staples.
- Smoothies: Milk is a fantastic base for smoothies. Combine it with fruits, vegetables, yogurt, and some sweeteners like honey or agave syrup for a nutritious and flavorful drink.
- Coffee and Tea: Many people enjoy adding milk to their coffee or tea. It can mellow out the bitterness and provide a creamier texture. You can use regular dairy milk or opt for non-dairy alternatives like almond, soy, or oat milk.
- Hot Chocolate: Make a cozy cup of hot chocolate by mixing milk with cocoa powder and a bit of sugar. You can even add whipped cream or marshmallows for an extra treat.

- Milk-Based Soups and Creamed Dishes: Milk can be used in various soups and creamed gravies, like creamy tomato soup, pasta, lasagna, and pot pies. It adds a rich texture and flavor.
- Milk in Cooking: Milk and milk products are common ingredients in many recipes. They are used in making pancakes, waffles, muffins, and various baked goods. You can also use it in savory dishes like mashed potatoes, sauces, and casseroles.
- Homemade Yogurt: If you make yogurt at home, milk is a key ingredient. You can use different types of milk, such as whole milk or 2% milk, to achieve your desired level of creaminess.
- Desserts: Milk is often used in dessert recipes. It’s an essential ingredient for making puddings, custards, ice cream, and a wide range of sweet treats.
Additionally, it’s important to be mindful of portion sizes and your overall daily caloric intake when incorporating milk into your diet.
Side Effects Of Milk
Certainly, it’s important to acknowledge the numerous health benefits of milk, it may have potential adverse effects for some individuals. Let’s take a look at these:
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common digestive issue where the body has difficulty digesting lactose, the sugar found in milk. This condition results from a deficiency of the enzyme lactase, which is needed to break down lactose in the small intestine. When lactose isn’t properly digested, it can lead to symptoms like bloating, gas, diarrhea, and stomach discomfort. However, there are lactose-free milk options and lactase supplements available for those who are lactose intolerant.
Milk Allergy
A milk allergy is different from lactose intolerance. It is an immune system response to the proteins in milk, such as casein and whey. Symptoms can range from mild, like hives or stomach upset, to severe, including anaphylaxis, which is a life-threatening reaction. If you have a milk allergy, you need to avoid milk and all milk products strictly. Fortunately, there are many non-dairy milk alternatives like almond, soy, oat, and coconut milk that can be used as substitutes.
Acne
There has been some debate about the potential link between milk consumption and acne. Some studies suggest that the hormones and growth factors in milk might influence skin health and lead to acne in certain individuals. However, this association isn’t universally accepted, and more research is needed to establish a clear connection. If you suspect milk may be contributing to your acne, you could consider reducing your dairy intake to see if it makes a difference.
Milk and Cancer
The relationship between milk and cancer is complex. Some studies have suggested that high dairy consumption, particularly in the form of whole milk, may be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, like prostate cancer. However, the evidence is not conclusive, and more research is needed to understand the underlying mechanisms. It’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about how milk consumption may affect your cancer risk.
Takeaway
Milk isn’t just a tasty treat; it’s a nutrient-packed elixir that brings a whole host of benefits to your life. With protein, minerals, fats, and vitamins in milk, it’s like a one-stop shop for health. So, whether you’re sipping on a classic glass of moo juice or trying out some nutty alternatives, here’s to enjoying the awesome health benefits that milk brings to the table. Order your favorite brands of milk and milk products from edobo today, Cheers!

0 Comment